The Employees’ State Insurance (ESI) Act of 1948 and the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act of 1952 are social security laws established by the Government of India. Their purpose is to offer social protection to workers in the organized sector.
The ESI Act offers medical, disability, dependent, and various other benefits to employees who are insured, while the PF Act guarantees financial security after retirement. Any establishment with 10 or more employees that pays wages within a certain limit must register with the appropriate regional ESI and PF offices.
Following this, all eligible employees must be enrolled. Registration enables both establishments and employees to access the benefits of the scheme. Ensuring timely contributions, maintaining accurate records, and conducting regular inspections are essential for effective implementation.
Who can apply?
Any individual or organization that employs workers for its operations in India is required to register for the ESI and PF schemes, provided they fulfill the eligibility criteria:
The subsequent points are applicable for ESI and PF registration in India:
- Individual proprietorships and partnership firms that employ 10 or more employees.
- Companies registered under Companies Act 2013, that employ 20 or more employees.
- Factories employing 10 or more workers and using power. Also 20 or more workers without using power.
- Shops, hotels, restaurants, cinemas including preview theatres, road motor transport undertakings and newspaper establishments employing 20 or more persons.
- Private educational institutions employing 20 or more persons.
- Medical institutions with inpatient beds employing 20 or more persons.
Furthermore, non-seasonal factories that have at least one employee are required to register under the PF Act.
After registration, these establishments must enroll within 15 days and ensure their eligible employees are included in the ESI and PF schemes. Foreign companies operating in India must also adhere to these regulations if they meet the specified criteria.
Documents Required for ESI and PF Registration
The essential documents needed for ESI and PF registration in India are as follows:
For ESI Registration:
- Registration Form 01 – Contains details like registration name, address, business activity, bank details etc.
- Proof of address – Copy of rental agreement, electricity bill, water bill, etc.
- Proof of incorporation – Copy of memorandum/articles of association, partnership deed, etc.
- List of employees and their dependents with Form 3, 3A, and 4.
- Resolution by Board of Directors for obtaining ESI registration.
For PF Registration:
- Registration Form 001 – Contains details like name, address, date of set up of the establishment, contact details etc.
- List of employees with names, ages, designations, departments etc.
- Proof of address (as mentioned above for ESI).
- Certified copy of Deed, Memorandum and Articles of Association, Partnership Deed, Trust Deed, Bye Laws etc. based on type of organization.
In addition to these, documents such as proof of identity for the owner or director, rent receipts, bank statements, and cancelled cheques may also be necessary in certain situations.
Government Fee
ESI Registration:
- No registration fees or charges
PF Registration:
- For establishments with up to 20 employees – No fees
- For establishments with 21 to 100 employees – 500 INR
- For establishments with 101 to 300 employees – 750 INR
- For establishments with 301 to 500 employees – 1000 INR
- For establishments with more than 500 employees – 1500 INR
Registration Process of ESI and PF
Here are the key steps to register for ESI and PF in India:
ESI Registration Process:
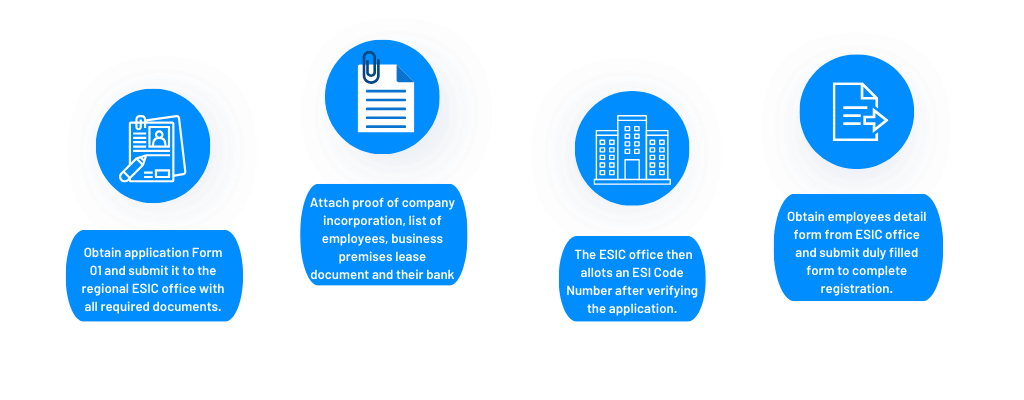
PF Registration Process:
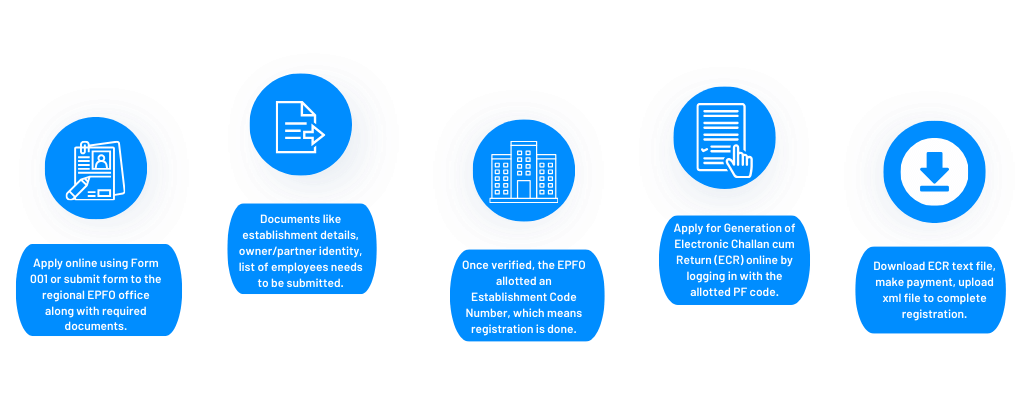
The distinctive code number assigned by the ESIC and EPFO offices should be utilized for all subsequent communications and for the submission of monthly and annual returns.
Employers are required to register eligible employees and commence the remittance of contributions.
Advantages of ESI AND PF Registration
The primary benefits of ESI and PF registration for both employers and employees are as follows:
For Employers:
- Registration is mandatory as per law, so it complies with regulations. Attracts good employees.
- Tax benefits as contributions paid is a deductible business expense.
- Enhanced loyalty and better productivity from social security covered employees.
- Staff absenteeism is reduced.
For Employees:
- Medical care and sickness benefits for self and dependents under ESI.
- Financial support to dependents in case of injury, funeral, unemployment and other contingencies.
- PF offers financial protection after retirement with pension and lump sum withdrawal.
- Peace of mind and work stability leading to increased efficiency.
- PF accumulations and even scheme benefits are easily transferable across organizations.
In conclusion, the registration for ESI and PF protects the interests of both employers and employees regarding compliance, productivity, and social security. It also reflects sound HR practices. Therefore, organizations that meet the applicable criteria should proactively register as soon as possible.
 Demos
Demos  Colors
Colors  Docs
Docs  Support
Support 



